Celiac.com 01/15/2024 - Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune condition primarily affecting the small intestine due to gluten sensitivity. Celiac disease exhibits various extraintestinal features, with the pancreas being one of the affected organs.
A team of researchers recently set out to provide a comprehensive overview of the pancreatic changes associated with celiac disease, with a particular focus on the exocrine aspect.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
The research team included Daniel Vasile Balaban, Iulia Enache, Marina Ciochina, Alina Popp, and Mariana Jinga. They are variously affiliated with the Department of Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania; Dr. Carol Davila Central Military Emergency University Hospital, Bucharest, Romania; the Department of Pediatrics, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania; and the National Institute for Mother and Child Health, Bucharest, Romania.
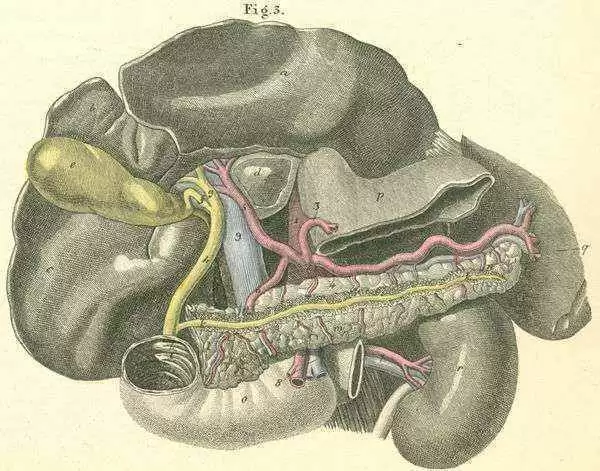
While pancreatic endocrine changes in celiac disease, especially in relation to type 1 diabetes mellitus, have been extensively studied, the attention to the exocrine pancreas has been comparatively limited. The review addresses several facets of pancreatic involvement in celiac disease.
Risk of Pancreatitis
The review explores the connection between celiac disease and the risk of pancreatitis. Understanding this association is crucial for managing celiac patients effectively.
Association with Autoimmune Pancreatitis
The link between celiac disease and autoimmune pancreatitis is examined. Autoimmune pancreatitis is considered in the context of celiac disease, shedding light on potential shared mechanisms.
Prevalence and Outcomes of Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency
The prevalence and outcomes of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency are discussed concerning both newly diagnosed and gluten-free diet-treated celiac disease patients. The impact of gluten-free diet adherence on pancreatic function is a notable aspect.
Link with Cystic Fibrosis
The review delves into the association between celiac disease and cystic fibrosis. Understanding this link is essential for comprehensive care, especially when dealing with concurrent conditions.
Mechanisms of Pancreatic Exocrine Impairment
The mechanisms behind the associated pancreatic exocrine impairment in celiac disease are explored. This includes an understanding of the pathological processes leading to pancreatic changes.
Recommendations for Clinical Practice
The review concludes by highlighting recommendations for clinical practice. These recommendations encompass the need for assessing pancreatic involvement in celiac patients and recognizing concomitant pancreatic diseases.
In summary, the review emphasizes that pancreatic alterations, encompassing both endocrine and exocrine aspects, are prevalent in celiac disease. Clinicians are urged to be vigilant for pancreatic involvement, and the recognition of concomitant pancreatic diseases in celiac patients is crucial for improving nutritional status and prognosis. Additionally, the review underscores the potential improvement in pancreatic function with a gluten-free diet, further emphasizing the importance of dietary management in celiac disease.
Read more in World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(24): 2680-2688






Recommended Comments
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now