Celiac.com 01/01/2026 - For many digestive conditions, early detection can dramatically improve treatment options and long-term outcomes. Yet current diagnostic methods, such as colonoscopies and other invasive procedures, can be uncomfortable, time-consuming, and difficult for many patients to access. A new study introduces an innovative approach that could change the landscape of gastrointestinal diagnosis: a swallowable capsule that uses engineered bacteria and magnetic hydrogel to rapidly detect signs of disease inside the gut. The technology aims to provide a gentle, fast, and highly sensitive way to identify biomarkers linked to various intestinal disorders.
The Need for a Gentler Diagnostic Method
Conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal cancer, and other digestive disorders often involve internal bleeding or inflammation within the intestines. Doctors typically rely on endoscopic procedures to visually inspect the gut and identify abnormalities. While effective, these methods require extensive preparation, are physically invasive, and can be stressful for patients. Many people put off screening because of these challenges, which delays diagnosis and allows disease to progress.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
Researchers have been searching for a way to collect reliable biological information from inside the gut without the discomfort of traditional procedures. One promising direction involves bacterial biosensors. Certain bacteria naturally react to environmental signals, making them useful for detecting chemical markers inside the body. However, safely and effectively delivering these bacteria to the gut has been a major challenge due to harsh digestive conditions and concerns about safety.
Developing a Magnetic Hydrogel System
To overcome these obstacles, the research team created a new platform called Magnetic Hydrogel Biosensor, which uses a soft, biocompatible material to protect and transport engineered bacteria. This hydrogel is made from alginate, a natural thickener that forms a stable gel-like structure. The gel encapsulates both magnetic particles and bacterial biosensors, forming tiny spheres that can be swallowed as part of a capsule.
The engineered bacteria inside the hydrogel were designed to recognize a specific molecule found in blood. When they encounter this molecule, which is associated with intestinal bleeding, they produce a visible glow. This light acts as a signal that can be measured after the hydrogel spheres are passed through the digestive system.
Because of the magnetic particles inside the hydrogel, the spheres can be easily separated from stool samples, allowing researchers or clinicians to quickly measure the amount of light the bacteria produced. The brightness of the signal correlates with the amount of bleeding inside the gut.
Testing the New Biosensor in Animal Models
The research team tested their magnetic hydrogel biosensor system in mice that had different severities of colitis, a form of intestinal inflammation commonly used to study gut disease. The mice swallowed the biosensor-containing capsule, and after it passed through the digestive tract, the hydrogel spheres were retrieved and analyzed.
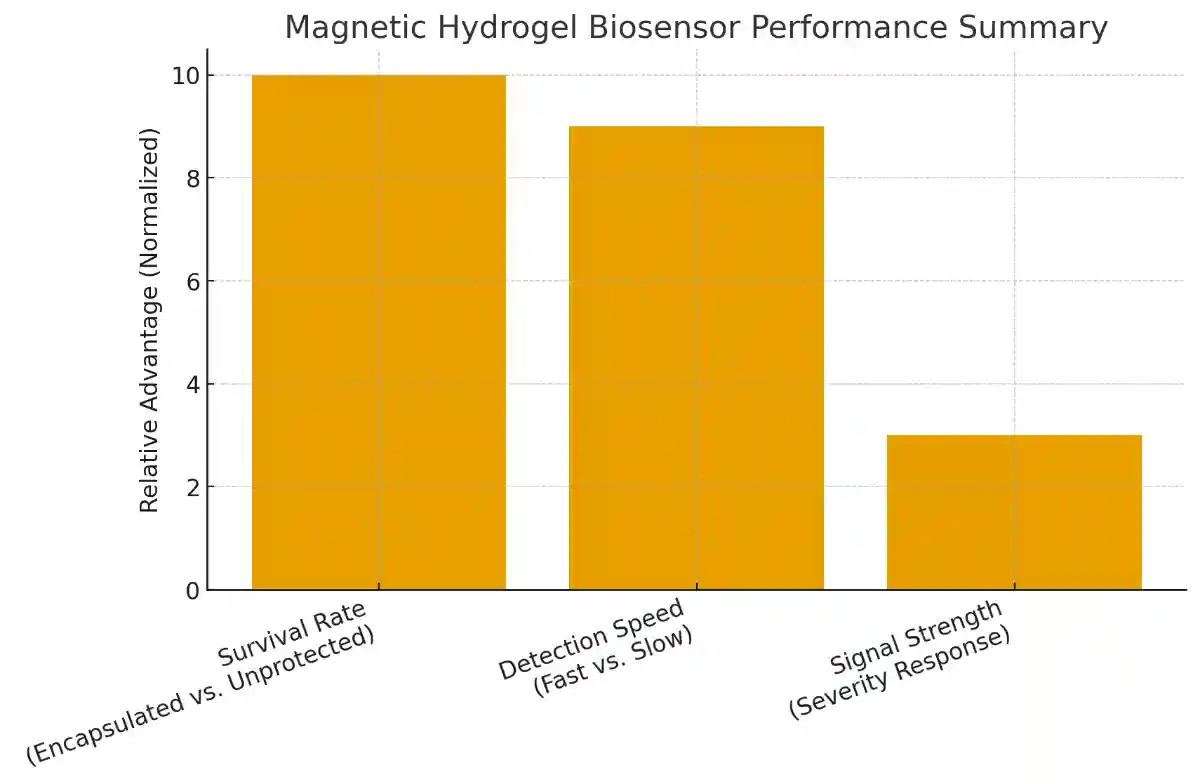
One of the most remarkable findings was how quickly the system detected intestinal bleeding. The magnetic hydrogel allowed the bacteria to remain stable and active inside the harsh environment of the stomach and intestines. Compared with unprotected bacteria, the hydrogel increased bacterial survival more than tenfold. As a result, the biosensor was able to detect bleeding within only twenty minutes. Traditional unencapsulated bacterial sensors required several hours to produce a detectable signal.
The light produced by the bacteria grew stronger as the severity of the disease increased. This meant the biosensor not only detected bleeding but also gave an indication of how severe the inflammation was. In addition, healthy mice showed no negative reactions to the hydrogel spheres, suggesting that the system was safe and well-tolerated during testing.
A Step Toward Noninvasive Gut Disease Monitoring
The study’s findings suggest that this magnetic hydrogel biosensor could eventually be used to diagnose or monitor a wide variety of gastrointestinal conditions. Because the platform is flexible, researchers believe it can be adapted to detect many different biomarkers, not just those related to bleeding. In the future, a single swallowable capsule might help identify inflammation, infection, or early signs of cancer.
Importantly, the method avoids the need for invasive procedures and can deliver results much faster than current testing approaches. It may help doctors catch disease earlier, personalize treatment, and monitor how well a person is responding to therapy. While human testing is still needed, the early results in animals demonstrate a strong potential for clinical use.
Implications for People with Celiac Disease
For individuals with celiac disease, this research is especially meaningful. Many people with celiac disease experience gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammation, and damage to the intestinal lining. Detecting these problems often requires procedures that can be uncomfortable or difficult to access. A swallowable biosensor pill could offer a fast, noninvasive way to check whether intestinal damage is occurring, whether a gluten-free diet is working, or whether complications such as refractory celiac disease might be developing.
Additionally, people with celiac disease sometimes struggle with delayed diagnosis because early symptoms can be subtle or mistaken for other conditions. A tool that identifies internal inflammation or bleeding quickly and easily could support earlier recognition and treatment. Ultimately, this new technology offers the possibility of more frequent monitoring, greater convenience, and earlier intervention, all of which could greatly improve outcomes for those living with celiac disease.
Read more at: pubs.acs.org










Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now