Celiac.com 08/28/2024 - Celiac disease is an immune-mediated disorder triggered by gluten consumption, leading to damage in the small intestine of genetically predisposed individuals. Despite its rising prevalence, many aspects of celiac disease remain unclear. One area of interest is the relationship between Candida albicans, a common yeast in the human gut, and celiac disease. This study explores how Candida can shift from a harmless presence to a potential pathogen, influenced by various factors within the body, and its implications for celiac disease.
Mast Cells and Their Role in Inflammation
Mast cells are part of the body's innate immune system and are abundant in the gastrointestinal tract. They act as sentinels, responding to environmental changes and helping to regulate immune responses. In the context of celiac disease, mast cells can contribute to inflammation and increased intestinal permeability. When mast cells are activated improperly, they release substances that disrupt the intestinal barrier, leading to inflammation. Studies have shown that individuals with celiac disease often have an increased number of mast cells in their intestines, which correlates with the severity of their condition.
Candida Albicans: Commensal or Pathogen?
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
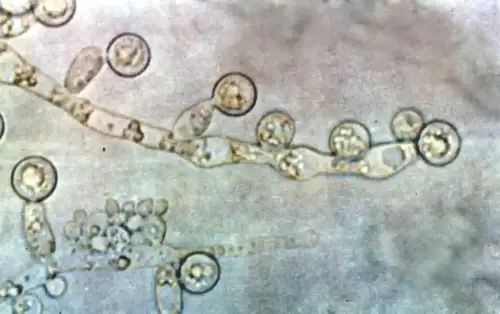
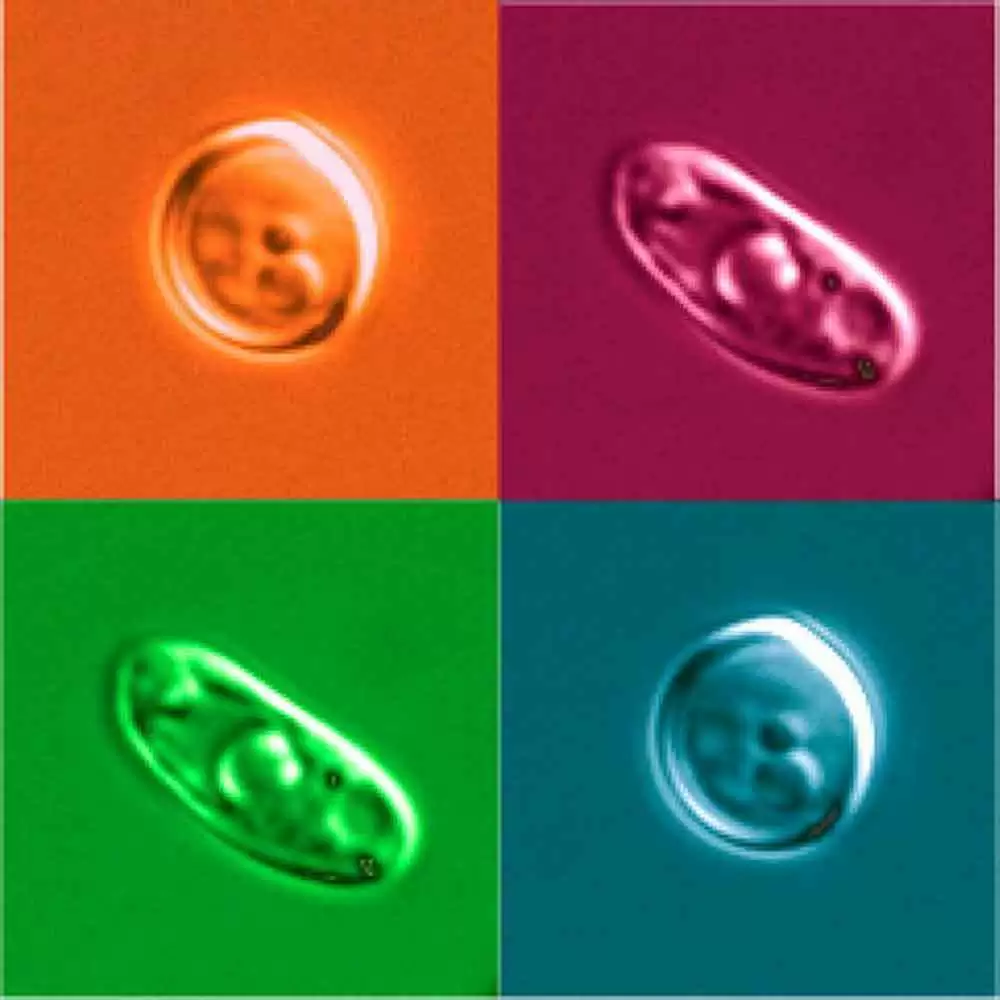
Candida albicans is typically a harmless resident of the gut, coexisting with the host's immune system and gut microbiota. However, under certain conditions, Candida can become pathogenic. Research suggests that Candida's transition from a commensal organism to a pathogen may be influenced by similarities between its components and gluten-related proteins that trigger celiac disease. This mimicry can activate the immune system inappropriately, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
Candida has been found in higher levels in individuals with celiac disease compared to healthy controls. This increased presence can exacerbate immune responses, potentially contributing to the intestinal damage seen in celiac patients. The ability of Candida to adhere to the intestinal lining and disrupt the barrier further complicates the situation, as it can promote a cycle of inflammation and increased gut permeability.
The Role of IL-9 in Candida and Celiac Disease
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) is a cytokine involved in regulating the immune system and maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier. In celiac disease, IL-9 levels are often elevated, which can lead to increased intestinal permeability and inflammation. IL-9 also influences the behavior of Candida, promoting its transition to a pathogenic state. This creates a feedback loop where increased IL-9 levels lead to more inflammation and Candida-related damage, worsening the symptoms of celiac disease.
Tryptophan Metabolism and Immune Regulation
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in maintaining immune balance in the gut. It can be metabolized by the host and gut microbiota into various bioactive molecules, including kynurenines and serotonin, which help regulate immune responses and maintain gut homeostasis. In celiac disease, disruptions in tryptophan metabolism can contribute to inflammation and impaired immune tolerance.
Research has shown that individuals with celiac disease often have altered gut microbiota, leading to changes in tryptophan metabolism. This can result in a reduced ability to control immune responses, further exacerbating the condition. Additionally, tryptophan metabolites like kynurenines can promote regulatory T cells, which help maintain immune tolerance. However, in celiac disease, the function of these regulatory cells may be impaired, contributing to ongoing inflammation.
Conclusion: Implications for Celiac Disease Patients
The study highlights the complex interplay between Candida albicans, the immune system, and tryptophan metabolism in the context of celiac disease. Understanding these relationships can provide new insights into potential therapeutic approaches for managing celiac disease. For individuals with celiac disease, maintaining a strict gluten-free diet is crucial, but addressing underlying factors such as Candida colonization and immune regulation may offer additional benefits.
This research is meaningful for celiac patients as it underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to managing the disease. By targeting factors like mast cell activation, IL-9 levels, and tryptophan metabolism, new treatments could be developed to reduce inflammation and improve gut health, potentially leading to better outcomes for those with celiac disease.
Read more at: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov





Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now